MADE for Datacenters
Design for 99.999% availability, manage thermal and electrical risk, and optimize maintenance across IT and facility infrastructure. With SLA penalties, high energy consumption, and multi-layered infrastructure, data centre operators face stringent demands on availability, diagnostics, thermal management and maintenance on key supporting assets like generators and fluid cooling systems. MADE can assist in supporting Datacenters to achieve their SLA’s and improve uptime and availablity.
Model-Based RAMS
for Datacenters Infrastructure
Purpose-built for complex infrastructure, the MADE platform empowers real-time reliability modeling, digital risk twin creation, and predictive maintenance across power, cooling, and computer systems. Accelerate ROI, minimize unplanned outages, and ensure compliance with stringent uptime, performance, and safety standards through model-based RAMS.

Benefits of MADE
Datacenters and Their Management
Why You Need MADE
How MADE Improves The Performance of Datacenters
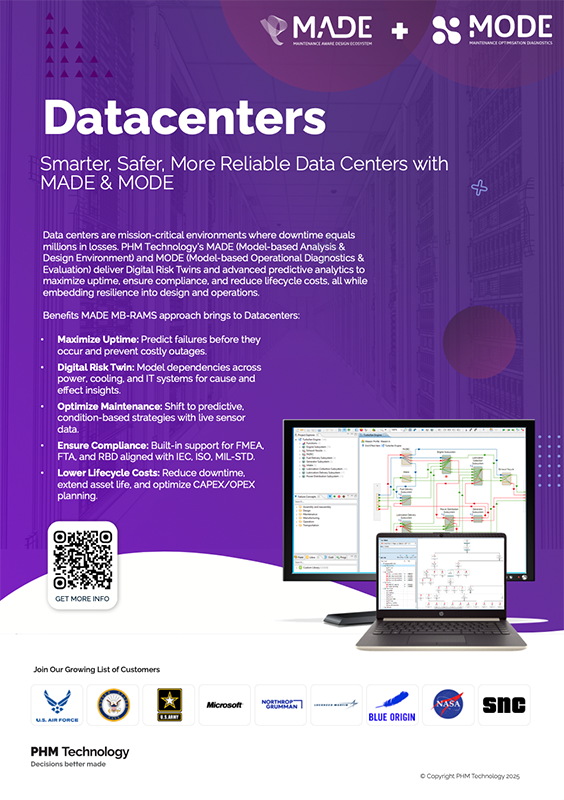
Digital Risk Twin for Critical Infrastructure
Model cooling, power distribution (UPS, PDUs, generators), and IT systems as a cohesive system. Identify interdependencies and simulate cascading thermal/electrical failures.
Real-Time Diagnostics and Fault Isolation
Integrate facility management system data for condition-based diagnostics. Use the Digital Diagnostic Twin (DDT) for rapid fault detection and response. Utilise the DDT to build a robust and executable predictive maintenance program to ensure maximum uptime.
Never Miss a Critical Failure
Create and define the optimum sensor design to capture and report every possible critical system failures.
Energy-Aware Risk Modeling
Assess how changes in thermal load, power usage effectiveness (PUE), and redundancy configurations affect risk and availability.
SLA Assurance and Reporting
Demonstrate compliance with SLA requirements using standardized availability analyses. Provide auditable reports to customers and regulators.
Rapid Fault Isolation and Restoration
Use the Digital Diagnostic Twin (DDT) to model fault propagation paths and identify critical isolation points in real-time. Supports automated root cause analysis, enabling faster recovery from grid disturbances.
Start Your MADE Software Journey Today
Let’s explore how the MADE Realibility Software can transform your engineering processes
Whether you have a specific challenge in mind or just want to learn more, we’re here to help. Fill out the form below and one of our experts will get back to you shortly with insights tailored to your needs.
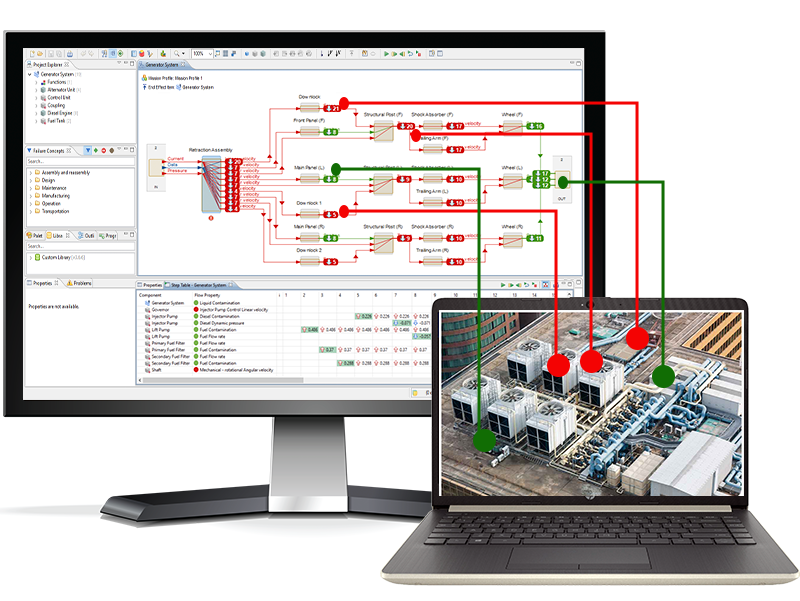
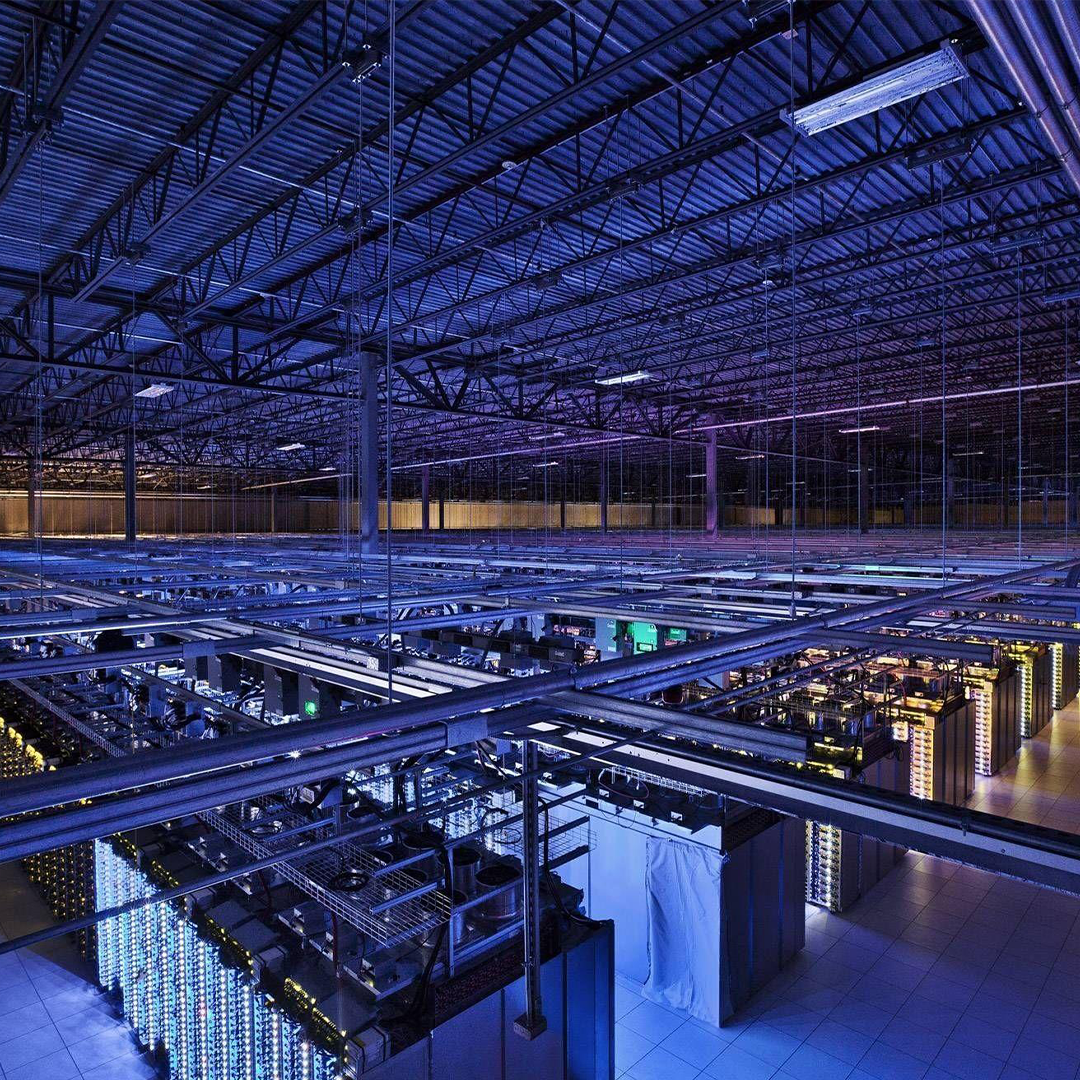
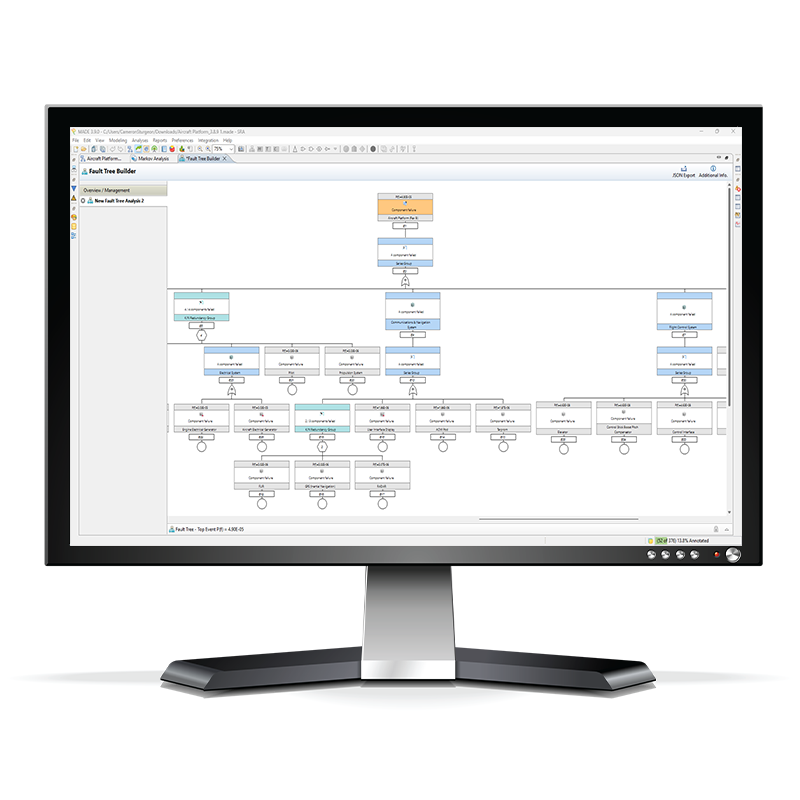
Fault Tree Analysis
At the touch of a button
MADE’s automated Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) helps you quickly identify and mitigate critical system risks consistently. By tracing failure pathways from top level events to root causes, MADE enhances safety, ensures compliance, and reduces downtime across the Datacenter. All at the touch of a button.

Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA)
Objective, faster and repeatable
MADE’s automated FMEA is an objective analysis that enables early detection of potential failure modes across critical datacenter systems. It supports design improvements, regulatory compliance, and reliability by identifying and addressing risks before they impact performance or safety. Its Model-based approach makes it high-integrity, rapidly repeatable as design and models update.
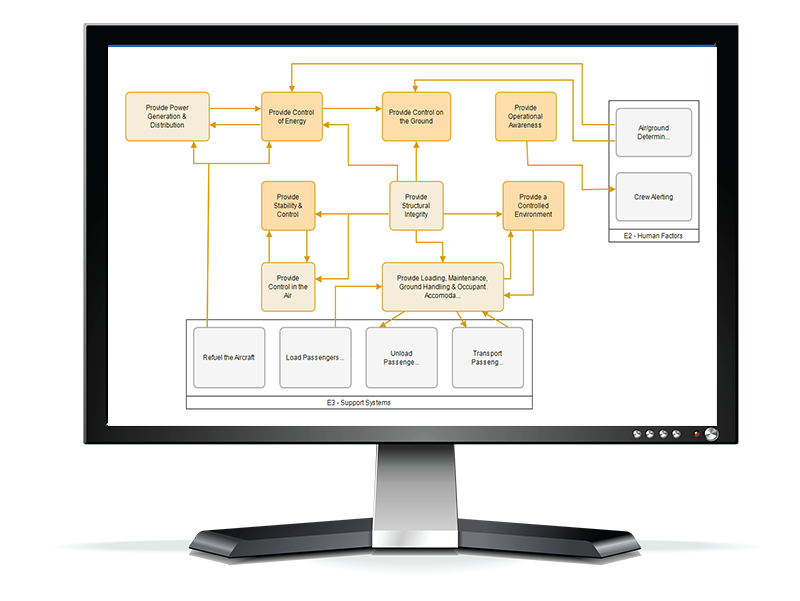
Functional Hazard Assessment
Better Power System Safety
MADE’s FHA helps datacenters assess and prioritize functional failures before they lead to hazards – At the design stage. It supports standards compliance and safer system design by linking functions to risks and identifying critical loss scenarios early, providing detailed traceability.
AI Datacenter Risks & How MADE Helps
Explore the key failure risks in AI data centers and how MADE supports reliable, available, and safe operations.
AI workloads (especially GPU-based training) generate extreme heat, stressing cooling systems beyond conventional loads. This increases risk of thermal failure and energy inefficiency.
How MADE Helps:
- Models dependencies between servers, power systems, and HVAC.
- Simulates cascading failures due to cooling degradation.
- Validates and optimizes cooling redundancy (e.g., N+1, 2N) in context of worst-case thermal loads.
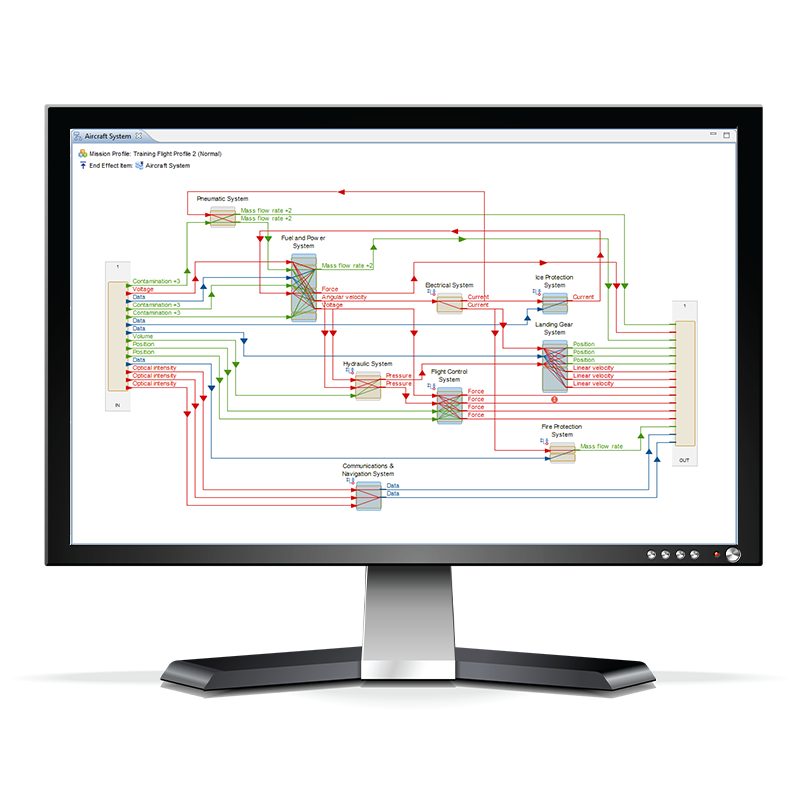
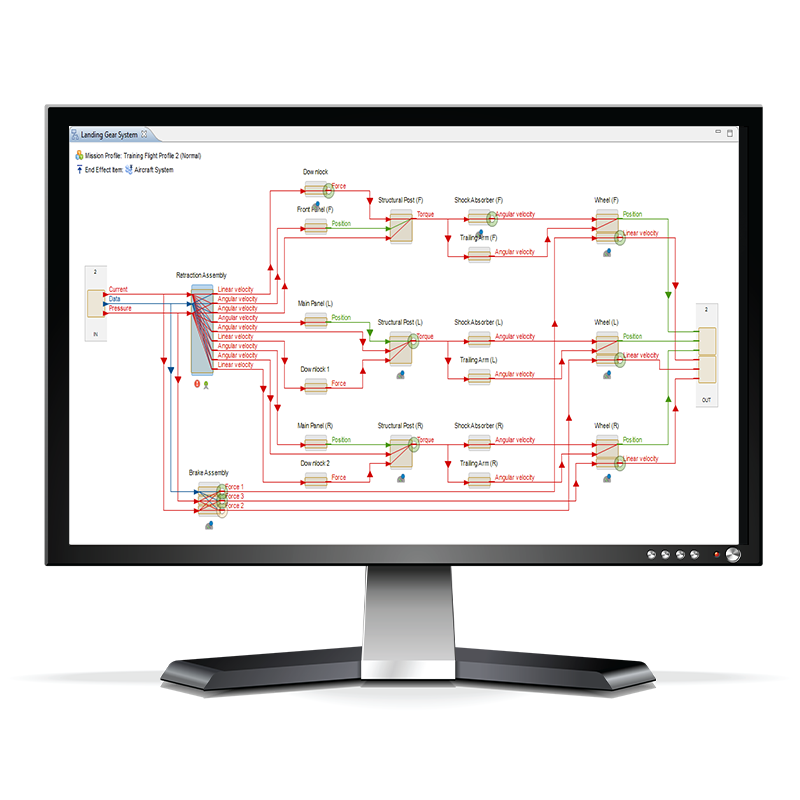
Datacenter Digital Risk Twin
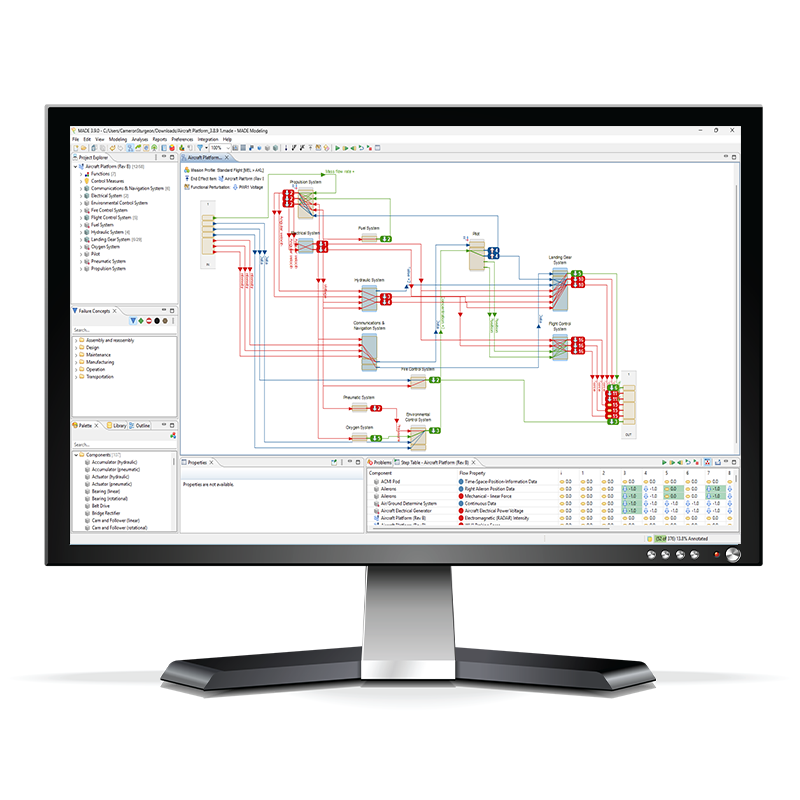
Cascading Failure Dependancy Map
Assessment of cooling redundancy strategies (N+1, 2N).
AI clusters demand extremely high-density power delivery with tight uptime SLAs. Multiple redundant systems (UPS, PDUs, gensets) introduce interdependent failure risk.
How MADE Helps:
- Creates a Digital Risk Twin to simulate electrical infrastructure failure propagation.
- Performs fault tree and RBD analysis across power topologies.
- Identifies weak points in redundancy architecture under load variance.

Digital Risk Twin
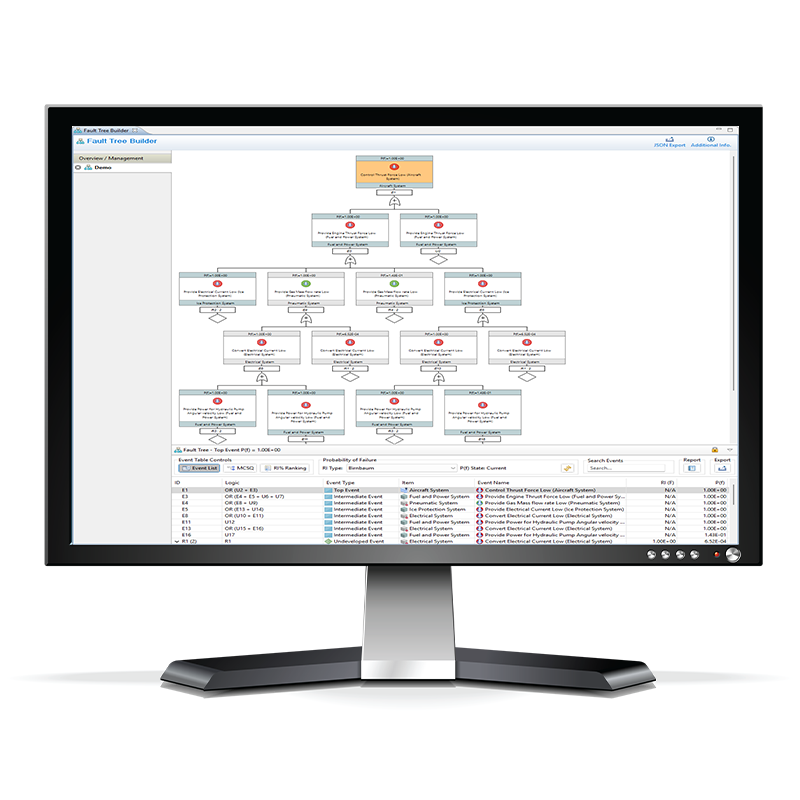
Fault Tree Analysis of critical power paths – Functional
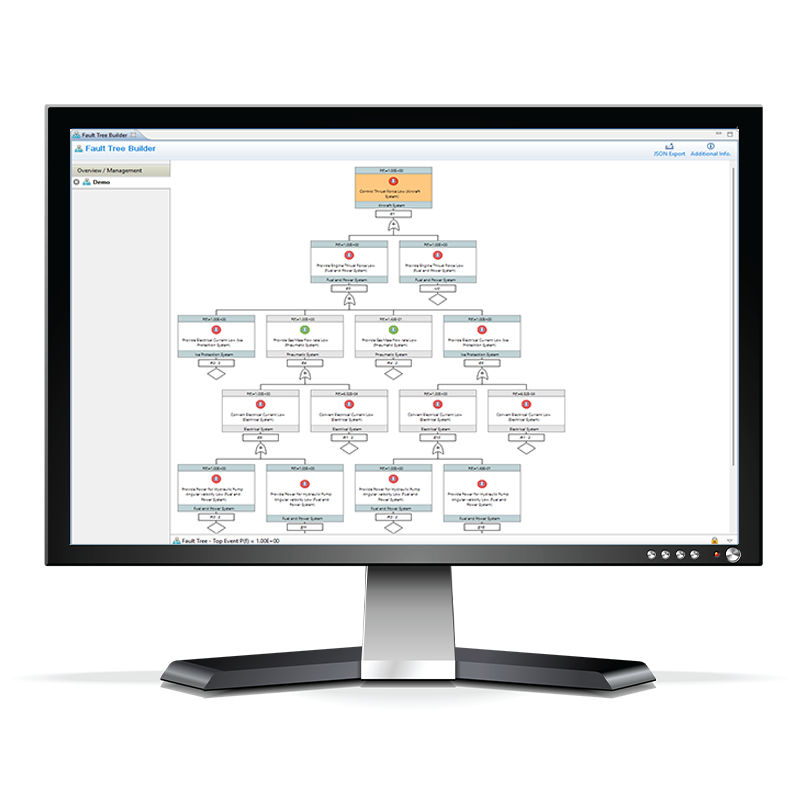
Fault Tree Analysis – Hardware
Rapid scaling of AI workloads creates diagnostic blind spots, where failures in cooling or power infrastructure aren’t detected until impact occurs.
How MADE Helps:
- Uses Digital Diagnostic Twins (DDTs) to verify sensor coverage, fault detection logic, and isolation time.
- Simulates fault scenarios and assesses MTTR to support resilient operations.
- Helps reduce diagnostic ambiguity and missed alarms.
Sensor coverage analysis across critical assets.
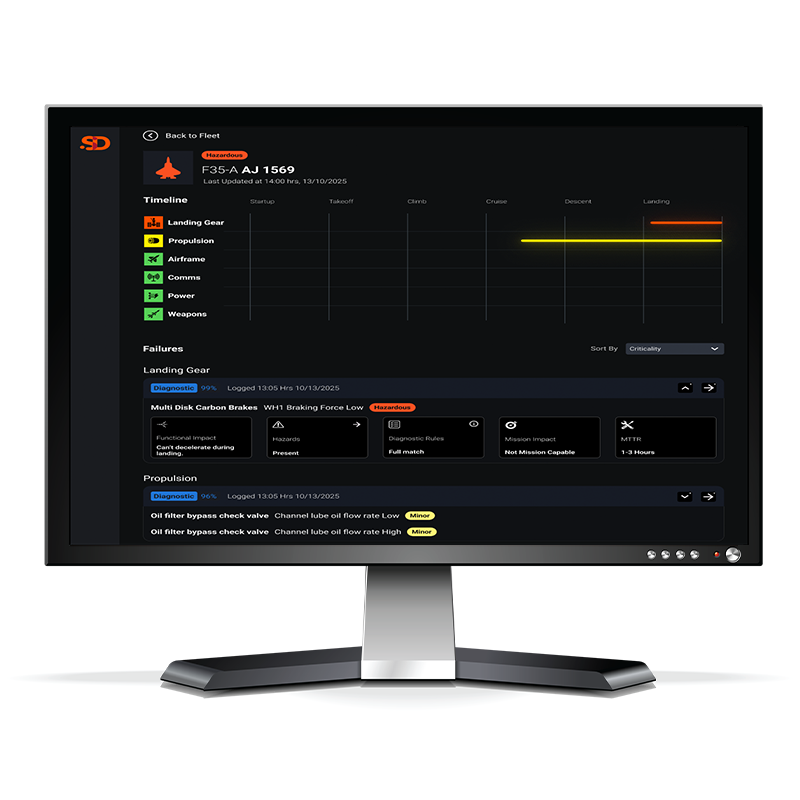
Fault Detection & Isolation
Simulated MTTR
AI downtime incurs significant financial and operational losses (due to model retraining needs, data loss, or SLA violations).
How MADE Helps:
- Supports CBM (Condition-Based Maintenance) validation to predict and schedule maintenance without over-servicing.
- Calculates availability under repair scenarios for SLA assurance.
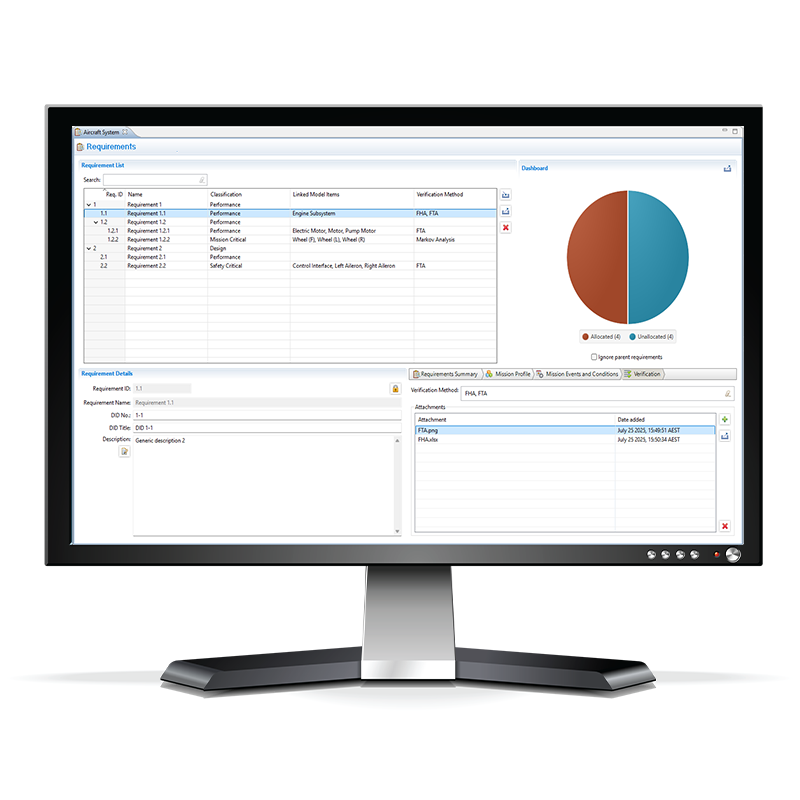
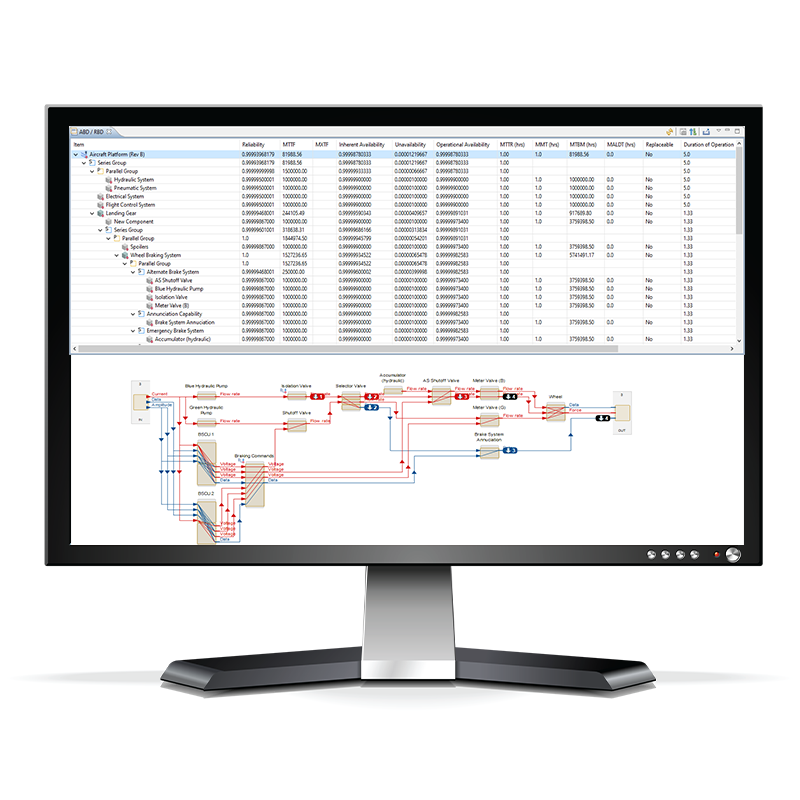
Requirements Verification

Cuasation-based FDI – Failure Prediction
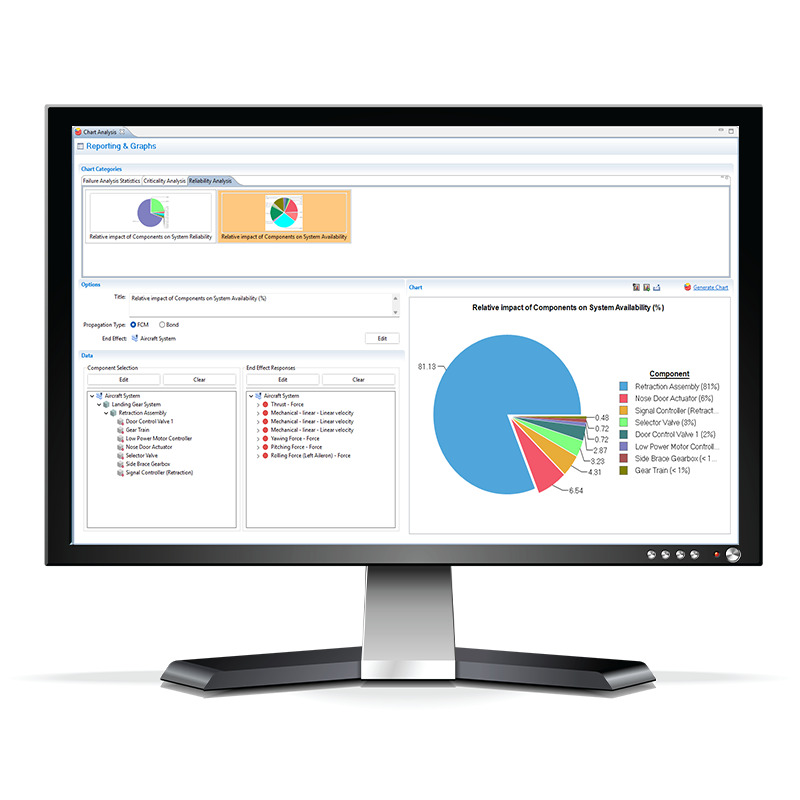
Availability dashboard for AI infrastructure.
AI workloads change rapidly, requiring reallocation of compute resources, cooling strategies, and power loads, which can introduce latent risks.
How MADE Helps:
- Models flexible, reconfigurable infrastructure scenarios and assesses associated risks.
- “What-if” trade studies across new workloads or hardware configurations (e.g., moving from NVIDIA A100 to H100 GPUs).
- Keeps RAMS artifacts synchronized with actual operational changes via MODE integration.
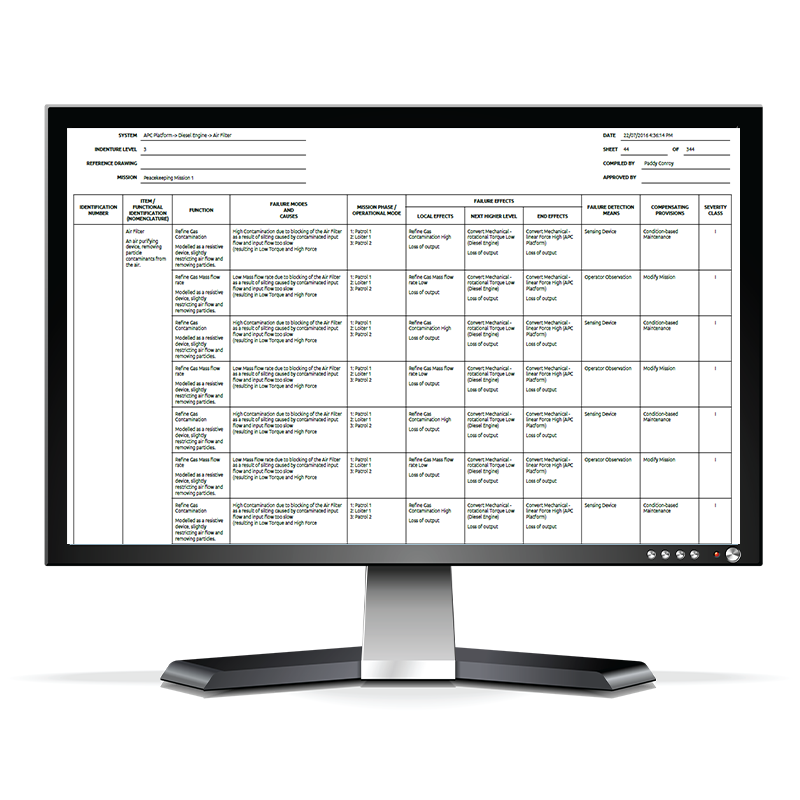
FMECA Analysis
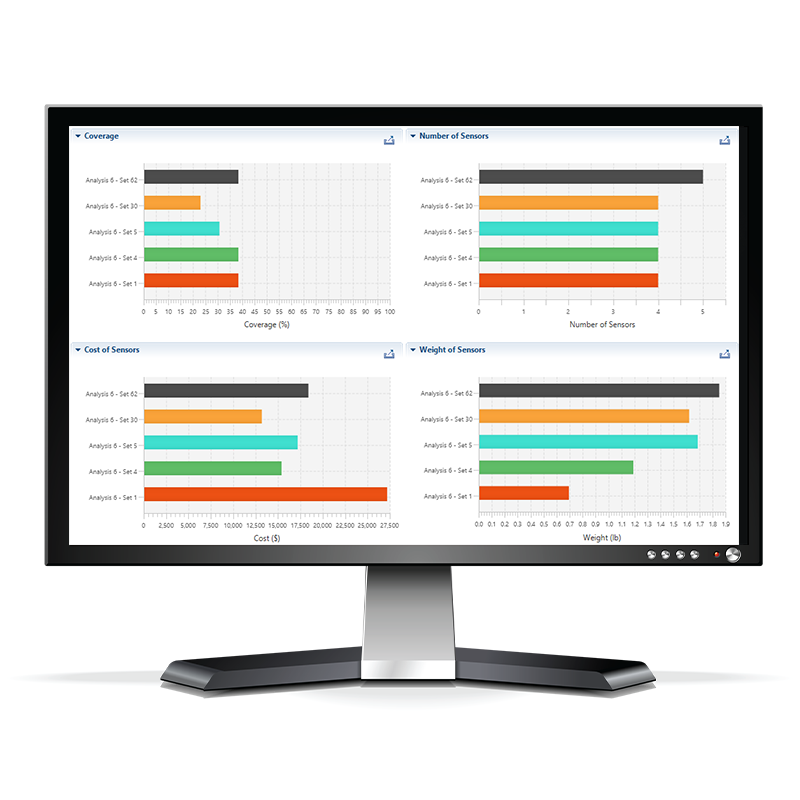
Sensor set trade studies
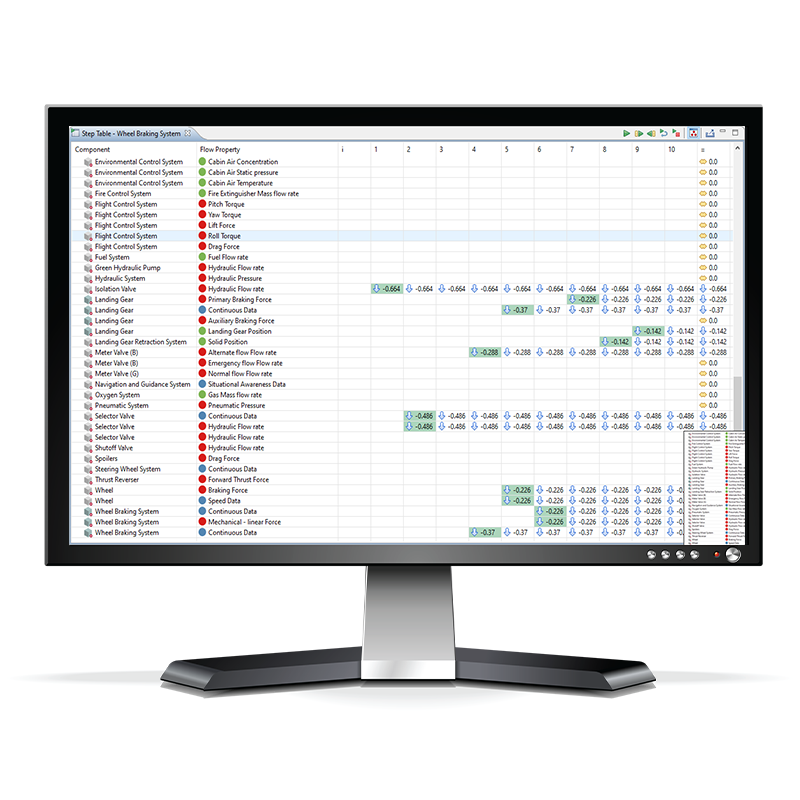
Failure Step Table